6-3 미니 배치를 사용하여 모델 학습
– 미니 배치 경사하강법
에포크당 모든 데이터를 사용하는 대신 작은 단계로 정방향 계산을 수행하고 기울기를 계산하고 가중치를 업데이트합니다.
작은 미니 배치로 가중치 업데이트
일반적으로 16, 32, 64와 같은 2의 배수가 사용됩니다.
– 미니배치 경사하강법 구현
1. MinibatchNetwork 클래스 구현
class MinibatchNetwork(RandomInitNetwork):
def __init__(self, units=10, batch_size=32, learning_rate=0.1, l1=0, l2=0):
super().__init__(units, learning_rate, l1, l2)
self.batch_size = batch_size # 배치 크기
2. Fit() 메서드 수정
def fit(self, x, y, epochs=100, x_val=None, y_val=None):
y_val = y_val.reshape(-1, 1) # 타깃을 열 벡터로 바꿉니다.
self.init_weights(x.shape(1)) # 은닉층과 출력층의 가중치를 초기화합니다.
np.random.seed(42)
# epochs만큼 반복합니다.
for i in range(epochs):
loss = 0
# 제너레이터 함수에서 반환한 미니배치를 순환합니다.
for x_batch, y_batch in self.gen_batch(x, y):
y_batch = y_batch.reshape(-1, 1) # 타깃을 열 벡터로 바꿉니다.
m = len(x_batch) # 샘플 개수를 저장합니다.
a = self.training(x_batch, y_batch, m)
# 안전한 로그 계산을 위해 클리핑합니다.
a = np.clip(a, 1e-10, 1-1e-10)
# 로그 손실과 규제 손실을 더하여 리스트에 추가합니다.
loss += np.sum(-(y_batch*np.log(a) + (1-y_batch)*np.log(1-a)))
self.losses.append((loss + self.reg_loss()) / len(x))
# 검증 세트에 대한 손실을 계산합니다.
self.update_val_loss(x_val, y_val)
3. gen_batch() 메서드 생성
# 미니배치 제너레이터 함수
def gen_batch(self, x, y):
length = len(x)
bins = length // self.batch_size # 미니배치 횟수
if length % self.batch_size:
bins += 1 # 나누어 떨어지지 않을 때
indexes = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(x))) # 인덱스를 섞습니다.
x = x(indexes)
y = y(indexes)
for i in range(bins):
start = self.batch_size * i
end = self.batch_size * (i + 1)
yield x(start:end), y(start:end) # batch_size만큼 슬라이싱하여 반환합니다.
4. 미니 배치 경사하강법 적용
minibatch_net = MinibatchNetwork(l2=0.01, batch_size=32)
minibatch_net.fit(x_train_scaled, y_train, x_val=x_val_scaled, y_val=y_val, epochs=500)
minibatch_net.score(x_val_scaled, y_val)
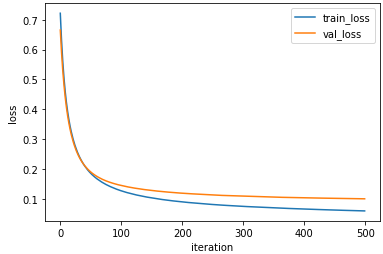
plt.plot(minibatch_net.losses)
plt.plot(minibatch_net.val_losses)
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('iteration')
plt.legend(('train_loss', 'val_loss'))
plt.show()

5. 미니 배치 크기를 늘려보십시오.
minibatch_net = MinibatchNetwork(l2=0.01, batch_size=128)
minibatch_net.fit(x_train_scaled, y_train, x_val=x_val_scaled, y_val=y_val, epochs=500)
minibatch_net.score(x_val_scaled, y_val)
plt.plot(minibatch_net.losses)
plt.plot(minibatch_net.val_losses)
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('iteration')
plt.legend(('train_loss', 'val_loss'))
plt.show()
※ MinibatchNetwork 클래스 코드
class MinibatchNetwork(RandomInitNetwork):
def __init__(self, units=10, batch_size=32, learning_rate=0.1, l1=0, l2=0):
super().__init__(units, learning_rate, l1, l2)
self.batch_size = batch_size # 배치 크기
def fit(self, x, y, epochs=100, x_val=None, y_val=None):
y_val = y_val.reshape(-1, 1) # 타깃을 열 벡터로 바꿉니다.
self.init_weights(x.shape(1)) # 은닉층과 출력층의 가중치를 초기화합니다.
np.random.seed(42)
# epochs만큼 반복합니다.
for i in range(epochs):
loss = 0
# 제너레이터 함수에서 반환한 미니배치를 순환합니다.
for x_batch, y_batch in self.gen_batch(x, y):
y_batch = y_batch.reshape(-1, 1) # 타깃을 열 벡터로 바꿉니다.
m = len(x_batch) # 샘플 개수를 저장합니다.
a = self.training(x_batch, y_batch, m)
# 안전한 로그 계산을 위해 클리핑합니다.
a = np.clip(a, 1e-10, 1-1e-10)
# 로그 손실과 규제 손실을 더하여 리스트에 추가합니다.
loss += np.sum(-(y_batch*np.log(a) + (1-y_batch)*np.log(1-a)))
self.losses.append((loss + self.reg_loss()) / len(x))
# 검증 세트에 대한 손실을 계산합니다.
self.update_val_loss(x_val, y_val)
# 미니배치 제너레이터 함수
def gen_batch(self, x, y):
length = len(x)
bins = length // self.batch_size # 미니배치 횟수
if length % self.batch_size:
bins += 1 # 나누어 떨어지지 않을 때
indexes = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(x))) # 인덱스를 섞습니다.
x = x(indexes)
y = y(indexes)
for i in range(bins):
start = self.batch_size * i
end = self.batch_size * (i + 1)
yield x(start:end), y(start:end) # batch_size만큼 슬라이싱하여 반환합니다.반응형
– 심령 실행으로 다층 신경망 훈련
1. MLPClassifier 객체 생성
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
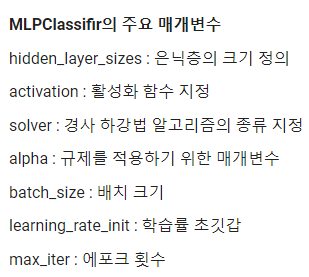
mlp = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(10, ), activation='logistic', solver="sgd", alpha=0.01, batch_size=32, learning_rate_init=0.1, max_iter=1000)
2. 모델 교육
mlp.fit(x_train_scaled, y_train)
mlp.score(x_val_scaled, y_val)
##출력: 0.989010989010989
※ 내용